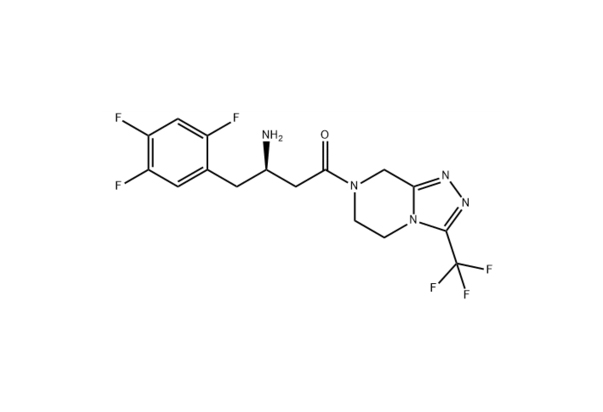
sitagliptinase
Cas N0. : 486460-32-6 Molecular formula: C16H15F6N5O
Production use
Pharmacodynamics
This drug is a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor that controls blood sugar levels by protecting and enhancing the effects of endogenous incretin. Glucose-dependent insulin-releasing peptide (GIP) and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), are incretins released in response to dietary intake.
GLP-1 and GIP can increase insulin synthesis and release from islet β cells through intracellular signaling pathways, and GLP-1 can also reduce islet α cells secrete glucagon to reduce hepatic glucose production. However, both GLP-1 and GIP are rapidly metabolized by DPP-4, resulting in a loss of their insulinotropic effects.
This drug inhibits the degradation of incretin by DPP-4, so it can enhance the function of GLP-1 and GIP, increase insulin release and reduce circulating glucagon levels (This effect is glucose-dependent). This drug selectively inhibits DPP-4, but has no inhibitory activity on DPP-8 or DPP-9.
Pharmacokinetics
The drug reaches a peak plasma concentration of 950nmol 1-4 hours after oral administration, the area under the curve is 8.52mmol·h, the absolute bioavailability is about 87%, and the protein binding rate is 38 %, the volume of distribution is about 198L. Rarely metabolized in the liver. The renal clearance rate is about 350ml/min, the renal excretion rate is 87% (79% is the prototype drug), and the elimination half-life is 12.4 hours. Hemodialysis helps to clear the drug.

